h1>
Ultrasound is one of the modern diagnostic and imaging techniques that allows specialists to perform accurate examinations of soft tissues. In terms of physiotherapeutic methods, ultrasound is a tool that guarantees precision for:
- Transcutaneous electrolysis EPTE treatment (Percutaneous electrolysis EPTE - MTS Holistic Therapy)
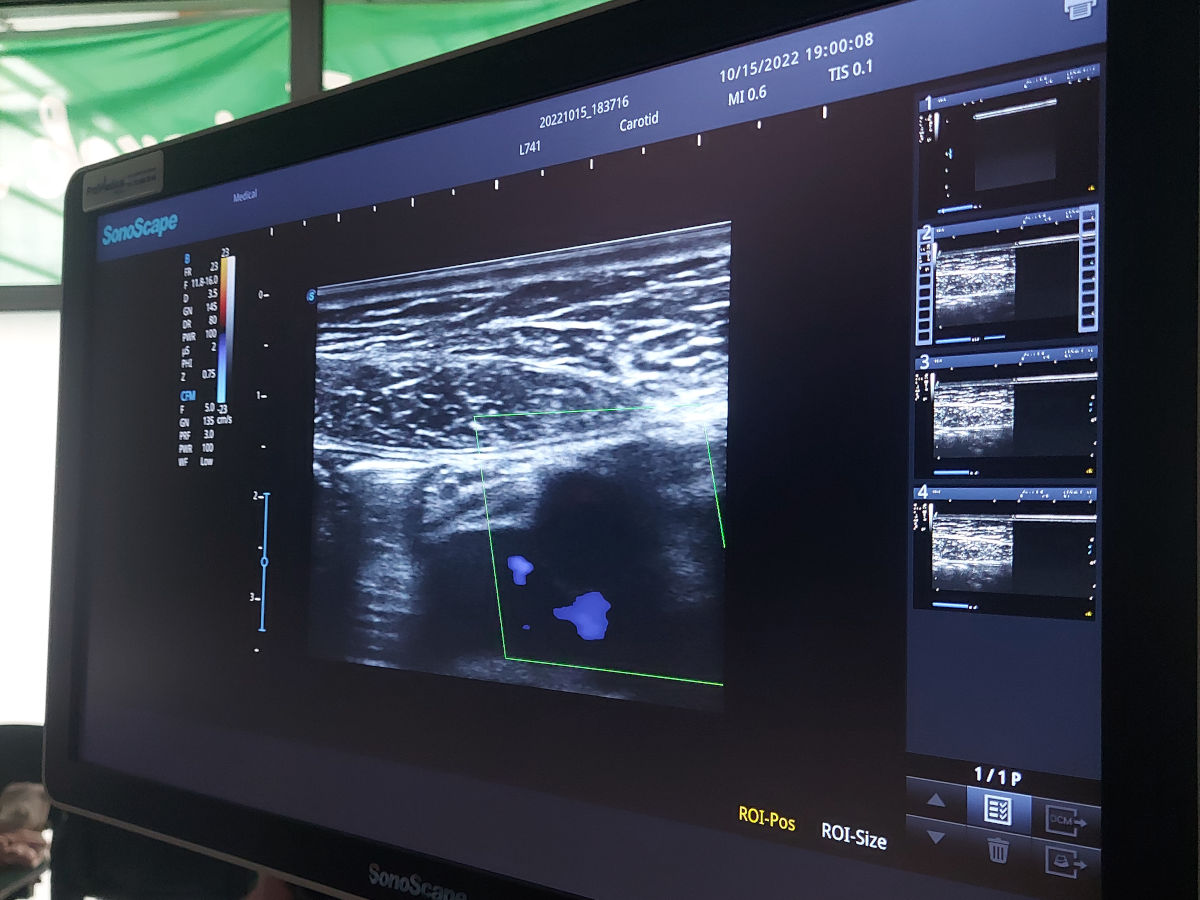
- Tissue diagnosis and assessment: - Diagnosis and assessment: Ultrasound for physiotherapy enables non-invasive assessment of soft tissues such as muscles, tendons, ligaments or joint capsules. Physiotherapists can accurately see anatomical structures, identify any damage or inflammation, and assess the degree of tissue regeneration. This allows them to fine-tune therapeutic plans and monitor the progress of treatment.
Therapy planning
Ultrasound imaging allows physiotherapists to better understand a patient's individual anatomical characteristics. This allows them to tailor therapeutic techniques to his or her needs, minimising the risk of injury or incorrect exercise technique.
Therapy management
Ultrasound helps visualise the biochemical and biomechanical processes occurring during therapy. Physiotherapists can track what changes occur in the tissues in response to the therapeutic techniques used, allowing them to adjust the treatment approach in real time.
Monitoring progress
Regular ultrasound examinations allow physiotherapists to monitor the effectiveness of the therapy. By comparing images from different periods of time, they can assess whether the therapy is having the desired effect and make adjustments if necessary.
Ultrasound provides an accurate assessment of soft structures and joints. Below are examples of disease entities and applications of ultrasound:
Muscle and tendon diseases
- Tendonitis (e.g. Achilles tendonitis)
- Muscle damage (e.g. muscle strain)
- Chronic inflammatory conditions (e.g. tendonitis)
Joint diseases
- Osteoarthrosis (joint degeneration)
- Arthritis (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis)
- Joint exudates (e.g. bursitis)
- Ligament injuries (e.g. rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee)
Diseases of the peripheral nerves
- Carpal tunnel (e.g. carpal tunnel syndrome)
- Nerve damage (e.g. compression of the ulnar nerve)
Fractures and injuries
- Assessment of soft tissue damage around fractures
- Detection of possible foreign bodies in wounds
- Tissue assessment after orthopaedic surgery
Therapy
- Percutaneous electrolysis EPTE
Are you struggling with chronic pain?
Take care of your health and well-being. Register for an ultrasound-guided EPTE Electrolysis treatment for physiotherapy. Find out more about our other treatment options
Soft tissue ultrasound has many benefits, both for the therapist or doctor in guiding treatment and for the patient themselves. The most important of these are:
- Non-invasive - Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging modality, meaning that it does not require puncturing or exposing the patient to ionising radiation. This is particularly important when examining children, pregnant women and radiation-sensitive patients.
- Accessibility - ultrasound is widely available in most medical facilities, making the diagnostic process easier and faster.
Real-time examinations - ultrasound allows real-time monitoring of soft structures and joints, enabling the clinician to observe tissue movement and function during the examination. - Soft tissue visualisation - ultrasound enables accurate assessment of muscles, tendons, ligaments, joint capsules and other soft tissues to detect damage, inflammation and other pathologies.
- Precision - ultrasound offers high image resolution, allowing for accurate localisation and characterisation of pathology.
- Monitoring treatment progress - ultrasound allows the physiotherapist to monitor treatment progress and assess the effectiveness of physiotherapy. Tissue healing and therapeutic effects can be monitored.
- Unique dynamic assessment - ultrasound allows dynamic assessment, i.e. assessment of structures during movement or loading. This is particularly important in physiotherapy, where patients often report pain or dysfunction during specific movements.
- No contrast - Unlike other imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound does not require contrast, which is beneficial for patients with allergies to contrast agents.
- Cost versus efficiency - ultrasound is often less expensive than other advanced imaging techniques, which can help reduce the cost of medical care.
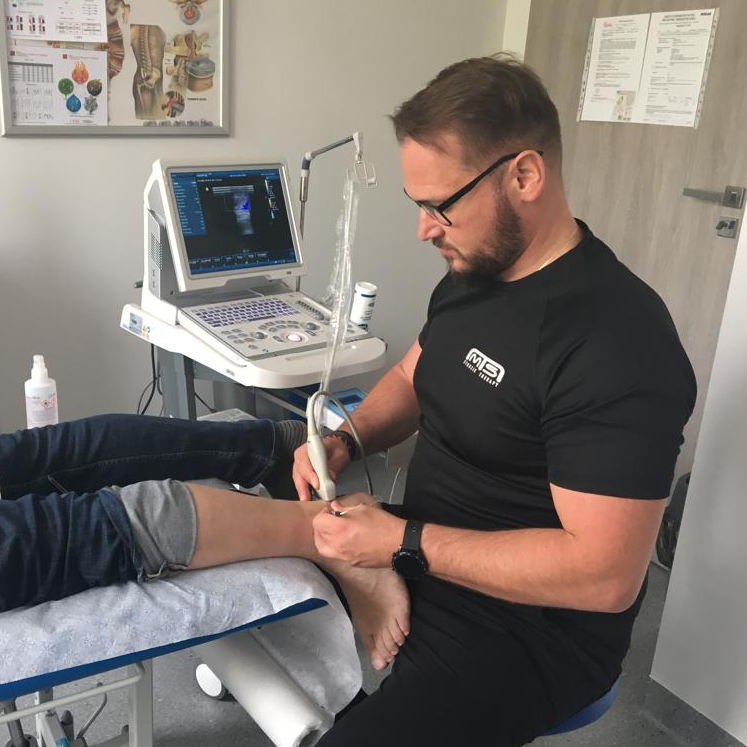
Rehabilitation Ultrasound Imaging (RUSI)
Ultrasonography (USG) is a versatile diagnostic tool that is used in many areas of medicine, including the practice of physiotherapists. Today's ultrasound technology enables precise analysis of soft tissues, giving physiotherapists a unique opportunity to assess anatomical structures and diagnose musculoskeletal conditions. In addition, ultrasound can be used in therapy, improving the effectiveness of treatments and monitoring patient progress.
The role of ultrasound in physiotherapy practice
Diagnosis and evaluation. Ultrasound enables a non-invasive assessment of soft tissues such as muscles, tendons, ligaments or joint capsules. Physiotherapists can accurately see anatomical structures, identify any damage or inflammation, and assess the degree of tissue regeneration. This allows them to fine-tune therapeutic plans and monitor the progress of treatment.
Therapy planning. Ultrasound imaging allows physiotherapists to better understand a patient's individual anatomical characteristics. This allows them to tailor therapeutic techniques to his or her needs, minimising the risk of injury or incorrect exercise technique.
Therapy management. Ultrasound helps visualise the biochemical and biomechanical processes occurring during therapy. Physiotherapists can track what changes occur in the tissues in response to the therapeutic techniques used, allowing them to adjust the treatment approach in real time.
Progress control. Regular ultrasound examinations allow physiotherapists to monitor the effectiveness of the therapy. By comparing images from different periods of time, they can assess whether the therapy is having the desired effect and make adjustments if necessary.
FAQ
Like many other manual therapies, pinopressure can cause some discomfort but is not painful. The technique involves gently pressing and massaging specific points on the body to stimulate the body's natural regeneration processes. Depending on the individual's sensitivity and degree of muscle tension, some people may feel some pressure, tingling or slight pain during a pinopressure session.
Like many other manual therapies, pinopressure can cause some discomfort but is not painful. The technique involves gently pressing and massaging specific points on the body to stimulate the body's natural regeneration processes. Depending on the individual's sensitivity and degree of muscle tension, some people may feel some pressure, tingling or slight pain during a pinopressure session.
Like many other manual therapies, pinopressure can cause some discomfort but is not painful. The technique involves gently pressing and massaging specific points on the body to stimulate the body's natural regeneration processes. Depending on the individual's sensitivity and degree of muscle tension, some people may feel some pressure, tingling or slight pain during a pinopressure session.
Like many other manual therapies, pinopressure can cause some discomfort but is not painful. The technique involves gently pressing and massaging specific points on the body to stimulate the body's natural regeneration processes. Depending on the individual's sensitivity and degree of muscle tension, some people may feel some pressure, tingling or slight pain during a pinopressure session.
Like many other manual therapies, pinopressure can cause some discomfort but is not painful. The technique involves gently pressing and massaging specific points on the body to stimulate the body's natural regeneration processes. Depending on the individual's sensitivity and degree of muscle tension, some people may feel some pressure, tingling or slight pain during a pinopressure session.
Like many other manual therapies, pinopressure can cause some discomfort but is not painful. The technique involves gently pressing and massaging specific points on the body to stimulate the body's natural regeneration processes. Depending on the individual's sensitivity and degree of muscle tension, some people may feel some pressure, tingling or slight pain during a pinopressure session.
Like many other manual therapies, pinopressure can cause some discomfort but is not painful. The technique involves gently pressing and massaging specific points on the body to stimulate the body's natural regeneration processes. Depending on the individual's sensitivity and degree of muscle tension, some people may feel some pressure, tingling or slight pain during a pinopressure session.
Like many other manual therapies, pinopressure can cause some discomfort but is not painful. The technique involves gently pressing and massaging specific points on the body to stimulate the body's natural regeneration processes. Depending on the individual's sensitivity and degree of muscle tension, some people may feel some pressure, tingling or slight pain during a pinopressure session.
Good to know
FIZJGuide
Advantages of RUSI
- Non-invasive
- Rapid exclusion of contraindications to rehabilitation
- Real-time feedback
- Widely used in rehabilitation, orthopaedics and sports medicine
The use of ultrasound in a physiotherapist's practice is a significant step towards more personalised and effective patient care. Ultrasound imaging allows for precise diagnosis, adaptation of therapeutic plans, monitoring of progress and guided therapy that translate into faster patient recovery and improved quality of life.
