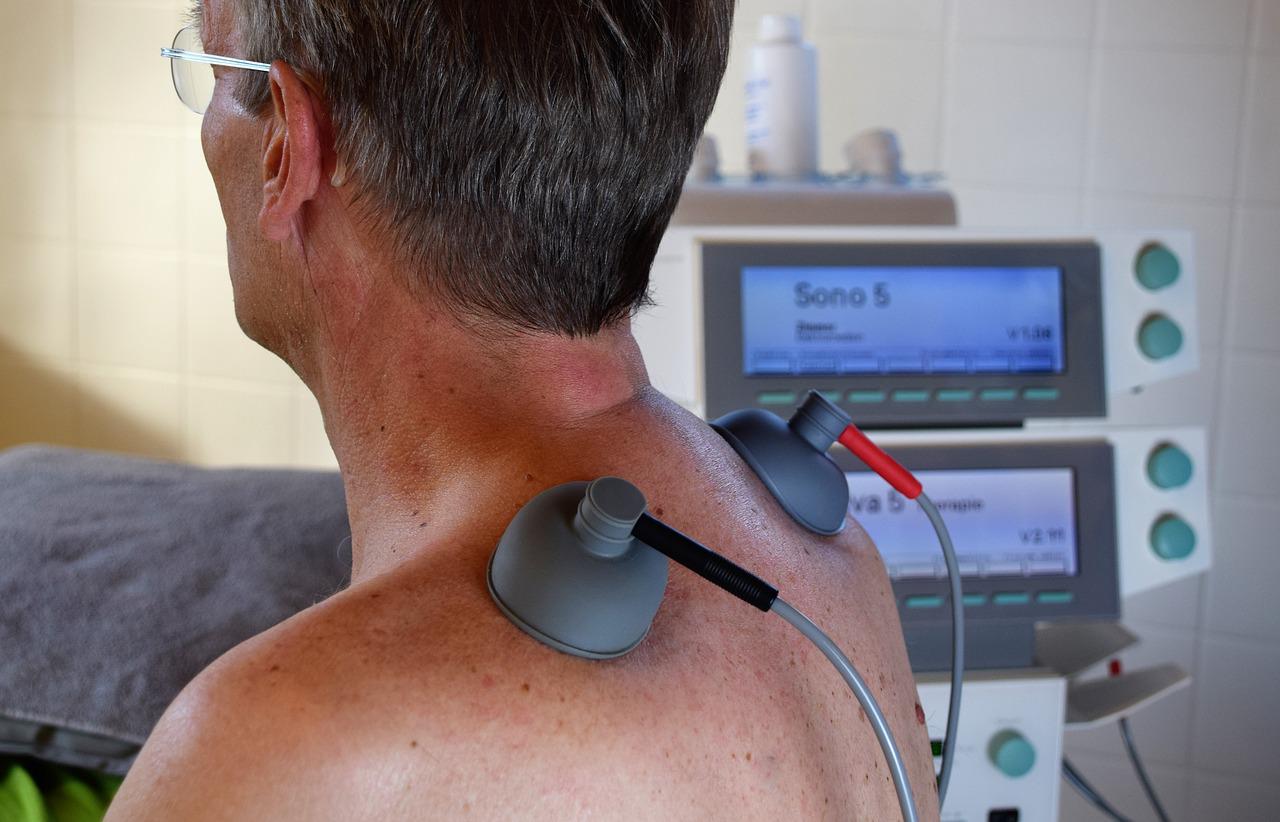
One of the rehabilitation procedures of high efficiency is therapy ultrasound, or sonotherapy. Properly conducted post-operative physiotherapy is a way to reduce the length of hospital stay, lower the risk of complications and return to daily life at full capacity more quickly.
What is ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a sound wave that has yes high frequency, that man is not in sthisnot hear them. It is known howeverthat they can be them emitted by certain animals, such as bats, dolphins, whales.
Discovery of the piezoelectric effect by Peter Curie in 1880 resulted in revolution in ultrasonic technology. He wasy one firstly used on ships for depth sensing and in metallurgy to identify cracks, but currently are often useda in medicine in which applicationnot ultrasound becomes wider and wider over time. There are wavesami mechanicalymi arisingymi due to the mechanical vibration of particles of an elastic medium at frequencies above 16kHz . However, frequencies such as 1MHz and 3MHz are primarily used in physical therapy.They are are sound waves inaudible to humans a Other than that, they do not differ in their properties from audible sounds.
Ultrasound in medicine
Ultrasound has been in widespread use since around the 1950s. It was first used for therapeutic purposes in 1938 to treat sciatica,
In rehabilitation, ultrasound is used at frequencies between 0.8 and 3 MHz. No electric current flows through human tissues during their application. The effectiveness of the therapy depends on the correct determination of the indications for their use, the use of the correct dose and the method of application. Ultrasound therapy is one of the best researched methods of physical therapy, as the efficacy of this treatment and the side effects that can occur when the therapy is applied incorrectly have been accurately recognised.
We distinguish between local or systemic ultrasound effects. During ultrasound treatments, there is a thermal effect, i.e. tissues are heated up, with nerve tissue overheating the most and muscle and fat tissue overheating slightly less. In contrast, heating tissues that have a high collagen content increases their elasticity without reducing their strength. Tissue heating also promotes accelerated repair processes in chronic inflammatory processes.
Other eThe effects of ultrasound can also be induced by stimulating the flow of intracellular and extracellular fluids. These mechanisms are attributed to anti-inflammatory effects and acceleration of repair processes.
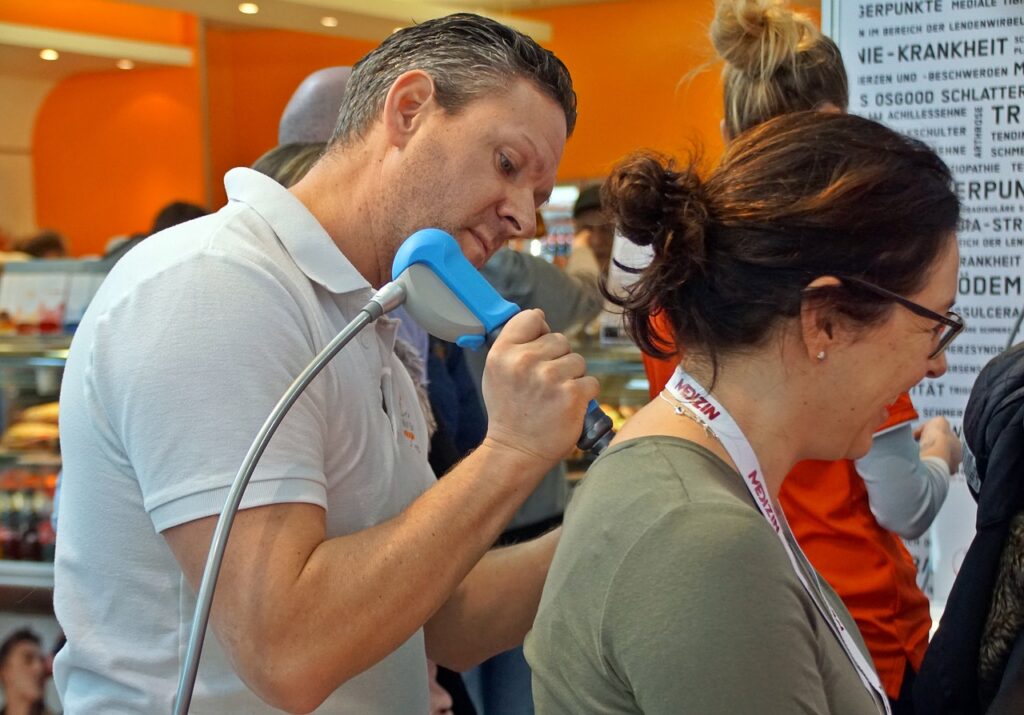

Use of ultrasound
Ultrasound has followinge effecti therapeutice:
- analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects,
- acceleration of lymph flow in the vessels and increased absorption processes,
- the generation of heat and a state of active congestion in the tissues,
- reducing muscle tension,
- inhibition of the sympathetic nervous system,
- Increased connective tissue extensibility in scars, contractures, fibrotic muscles and joint capsules,
- accelerating wound healing.
Therefore shall be used of which in the case of:
- post-traumatic conditions,
- inflammatory conditions,
- osteoarthritis of the spine and joints,
- heel spurs,
- treatment of lymphoedema,
- rheumatic diseases,
- treatment of contractures i scars.
Ultrasound - contraindications and side effects
Both ultrasound and infrasound can have negative effects on the human body. If applied in the wrong way, they can be harmful: causing circulatory problems, damaging hearing, and causing dizziness and headaches . This treatment must not be used during pregnancy or on children. The application of ultrasound waves to the area around the eyes, the skull and the medulla oblongata is also inadvisable. These can cause headaches, dizziness, hearing damage or constipation.
Ultrasound cannot be used in cancer patients. Other contraindications to the use of this method are:
- active tuberculous processes,
- haemorrhagic diathesis,
- circulatory insufficiency and cardiac arrhythmias,
- severe general condition and cachexia,
- uncompleted bone growth in the growth disc area,
- neuralgia of unexplained origin,
- acute inflammatory processes and febrile conditions,
- diabetes,
- thrombophlebitis,
- disorders of the peripheral blood supply,
- neuropathies,
- intervertebral disc prolapse,
- conditions after excision of the vertebral arch,
- blood clotting disorders.
- pregnancy.
- implanted pacemaker
- osteoporosis.