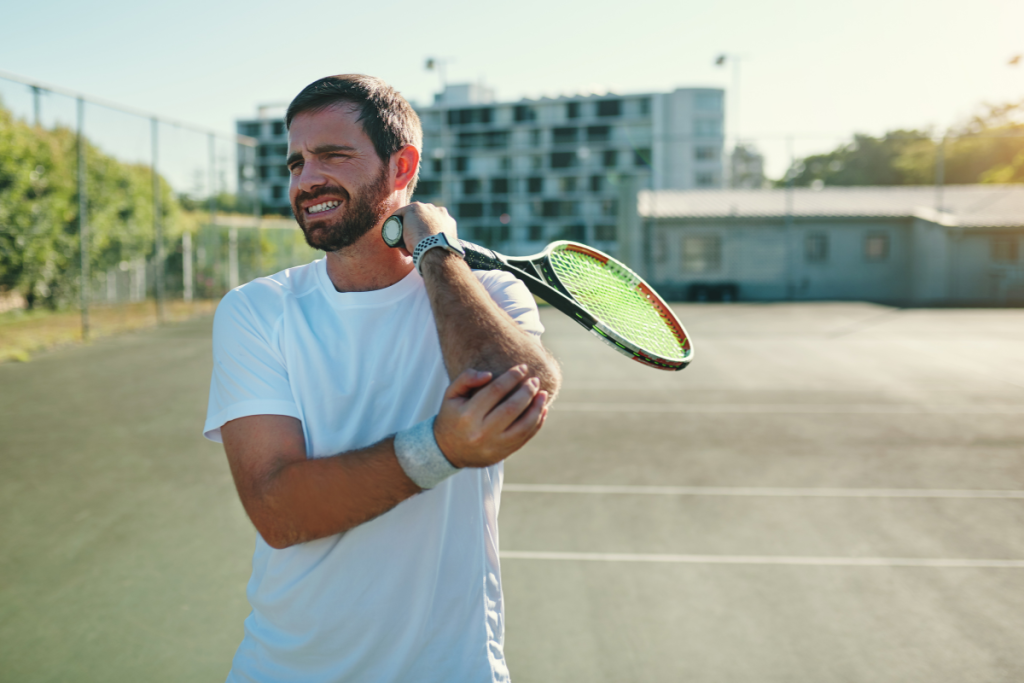
Elbow pain can be caused by various injuries and traumas, but it can also be a symptom of osteoarthritis and inflammation in the elbow area. It is often associated with overuse of this part of the body, as many sports require repetitive, monotonous movements of the elbow, hand or arm. However, as it turns out, it does not only affect athletes and can affect anyone, regardless of age.
How is the elbow joint structured?
The elbow joint is the anatomical connection between the shoulder and forearm and is formed by three pairs of articular surfaces surrounded by a common joint capsule and reinforced by ligaments. It is a complex, hinge-rotation, biaxial joint. It allows flexion of the upper limb and rotational movement of the forearm.
Who is most commonly affected by elbow pain?
The most common cause of elbow pain can be micro-injuries and inflammation. People who play tennis, squash, badminton and golf are at risk of developing elbow pain because they are constantly performing the same movement sequences. Repetition also increases the risk of elbow pain for dentists, masseurs, programmers, office workers and carpenters. Cooks, lumberjacks and archers are also at risk. Elbow pain mainly results from prolonged overloading of the arm during wrist movements. Degeneration of the elbow joint also contributes to it. It is worth noting that usually the hand that starts to hurt is the dominant limb, which is usually the right.
Elbow pain - what are the most common causes?
The most common injuries causing symptoms of a painful elbow include:
- elbow fracture,
- fracture of the ulnar process,
- sprain and dislocation of the elbow.
Pain in the elbow joint, with pain in the hand and a swollen elbow, can also be caused by osteoarthritis and inflammation of the tendons, known as tendinopathies, and inflammation of the tendon attachments, or enthesopathies. The latter include conditions such as golfer's or tennis elbow. Such pain can also be caused by elbow bursitis. Other causes include entrapment of nerve structures and impaired mobility between tissues. Overall, the most common causes of elbow pain include:
- tennis elbow,
- golfer's elbow
- ulnar nerve canal syndrome,
- Guyon's canal syndrome,
- dislocation or fracture of the elbow,
- capsulitis,
- arthritis,
- rheumatoid arthritis
- osteomyelitis,
- diseases such as lupus or Lyme disease.

Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that can lead to inflammation of the joints, including the elbow joint. In RA, the immune system attacks the joint tissues, causing pain, swelling and stiffness. Symptoms of RA in the elbow can include pain, limited joint mobility and structural changes such as joint deformities. Treatment RA involves the use of disease-modifying drugs (DMARDs), corticosteroids, painkillers and physiotherapy. The aim of treatment is to reduce inflammation, control pain symptoms and prevent joint damage.
Elbow bursitis
The elbow bursa is a small fluid-filled sac that is located on the back of the elbow and acts as a shock absorber between the skin and bone. Bursitis, also known as elbow bursitis, can occur as a result of injury, overuse or infection. Symptoms of elbow bursitis include swelling, pain and redness in the elbow area. If infected, a fever and purulent discharge may occur. Treatment Elbow bursitis usually involves rest, avoiding pressure on the elbow, using anti-inflammatory medication and. In some cases, the specialist recommends fluid aspiration or antibiotic therapy in case of infection.
Elbow pain - treatment
The factor that causes elbow pain determines how it is treated. Often, conservative treatment, i.e. rest and a change in habits, as well as the use of elbow pain ointments, analgesic and anti-inflammatory tablets and various physiotherapy treatments, is sufficient. W rehabilitation elbow joint injuries specialists use both physical therapy methods and treatments manual therapy. In addition, treatments to strengthen and improve the mobility of the joint and its components.
Among the physical therapy treatments for proximal elbow pain are iontophoresis, which involves the administration of a painkiller by means of electricity, laser or ultrasound. On the other hand, if the patient suffers from tennis elbow, shock wave therapy can be used. Very effective treatments for elbow problems are massages. Mainly relaxing tight muscles, tendons of the arm and forearm. New methods for soothing elbow pain include. kinesiotaping involving the application of plasters to the painful area. It helps to pull the skin and fascia away from the muscle structures and increase the space in the elbow joint area. This causes the pain to ease and sometimes even disappear.
In more difficult, advanced cases or those that do not lend themselves to conservative treatment, the specialist opts for surgical treatment.